Types of Cells:
- Prokaryotic
- Bacteria
- Archaea

2. Eukaryotic
- Unicellular
Protists
- Multi-cellular
Fungi
Plants
Animals
Bacteria
Characteristics
- Greek for "small stick"
- Most Abundant Organism
- Found in all Media
- Many are Pathogens
- Move by Flagella or by Gliding
- Asexual Reproduction
- Beneficial in Everyday Needs
Archaea
Characteristics Greek for “old ones”
Identified in 1977 by Carl Woese of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and George Fox Extremophiles Mesophiles Found in Living Organisms Two Groups: Euryarchaeota and Crenarchaeota
Fungi
Characteristics
All come from a common ancestor
Thought to be more related to animals then plantsMost are symbioticLacks organsReproduce sexually or asexuallyMany are used in everyday human life

Plant Cells
Characteristics- Has a cell wall made of cellulose
- Has a large central vacuole
- Undergoes photosynthesis
- Contains Chloroplasts which contain Chlorophyll
- The cells differentiate in to dermal tissue, vascular tissue, or ground tissue
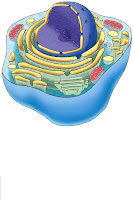
Animal Cells
Characteristics
Unicellular and Multicellular
Lacks a Cell Wall and ChloroplastsSmall Vacuoles Appear spherical in shapeContains a variety of Organelles




Tiada ulasan:
Catat Ulasan